Injection technique
proper insulin delivery to the tissue
Avoidance of complications
The correct injection technique ensures the correct delivery of insulin into the tissue, the timely release of insulin in the body, and thus the avoidance of complications.
Choice of injection site
Injections have to be done into the fatty tissue of the skin (subcutaneous) to ensure best availability of the insulin.
Appropriate injection sites
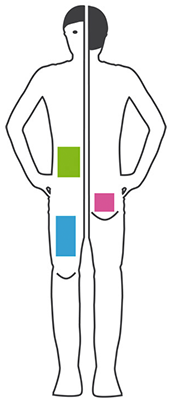
Insulin can be injected in different sites of the body. Your doctor will recommend you to inject insulin in your thigh, the belly, the buttocks or in the upper arm. Within the chosen area it is recommended to change the injection sites. Otherwise skin irritations or swellings can occur and it will be more difficult to predict the effect of the insulin.
Quick acting insulins (insulin analogues and mixed insulins) should be administered to the following sites:
- Belly
- Tigh
For slow acting insulin (insulins with delayed action or mixed insulins) the recommended injection site is:
- Backside
Rate of insulin resorption
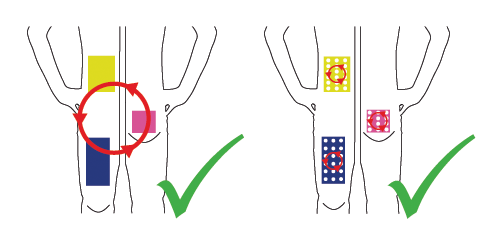
Injections in the arm are not recommended with the exception that an assisting person performs it by holding a skin fold. It is recommended to use within the day different injection sites within an area. Every new injection should be at a distance of one fingerbreadth from the last injection site.
Change weekly between left and right half of the body. There exist rotating patterns which assist correct injections in belly and thigh (for children and adults) in our Download-Area.
Insulin Delivery Recommendations
The 4-mm needle is long enough to traverse the skin and enter the subcutane tissue, with little risk of intramuscular (or intradermal) injection. Therefore, it is considered the safest pen needle for adults and children regardless of age, sex, ethnicity, or BMI.
The 4-mm needle should be inserted perpendicular to the skin (at 90° to the skin surface), not at an angle, regardless of whether a skinfold is raised.
Very young children (<=6 years old) and very thin adults should use the 4-mm needle by lifting a skinfold and inserting the needle perpendicularly into it. Others may inject using the 4-mm needle without lifting a skinfold.
Frid AH, Kreugel G, Grassi G, Halimi S, Hicks D, Hirsch LJ, Smith MJ, Wellhoener R, Bode BW, Hirsch IB, Kalra S, Ji L, Strauss KW. New Insulin Delivery Recommendations. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016 Sep;91(9):1231-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.06.010. PMID: 27594187.
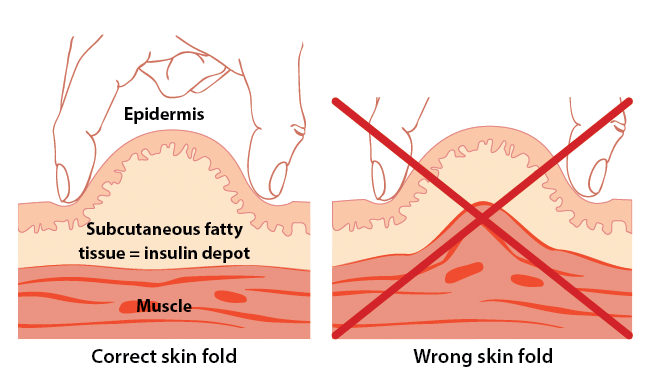
Injection with Skin Fold
To ensure injection in subcutaneous tissue and not in muscle tissue it is recommended to hold a skin fold and inject in here. In that case longer pen needles can be used. The injection angle can be 90° or 45° - depends on what the person prefers. To hold the skin fold correctly only thumb and forefinger should be used. Only skin and subcutaneous tissue should be taken by leaving muscle tissue.
The reuse of pen needles can be dangerous!
Crystallized insulin from a previous injection can block the needle and lead to an inaccurate insulin dosage.
Use a new pen needle for each injection!
With a fresh pen needle for each measurement, you yourself can ensure that the injection is as painless as possible. Pen needles have microfine tips which are damaged after only one use. With each further use, the pen needles become blunter and form small barbs. This makes further punctures more painful and can even damage the tissue, leading to lipohypertrophy. The sliding coating on the pen needle will be worn away with the first injection, reuse may cause unnecessary pain.
Pay attention to hygiene.
The pen needle is a sterile disposable product and should only be used once. With each injection, tiny traces of blood and tissue, which can only be seen under a microscope, remain on the pen needle. We therefore advise against using the pen needle more than once.
Storing Insulin Correctly
Insulin is sensible against environmental impacts. Not used insulin should be stored in the “vegetables” compartment of the refrigerator at 4-8°C. Take care that it never freezes (even not for a short time). To prevent burning sensation caused by injection of cold insulin you can store the bottle, vial or syringe with insulin in use at room temperature making sure that it is protected against direct sunlight and heat. The full effect if insulin is ensured over a period of a minimum of 4 weeks.
If you have to stay at very low or high temperatures for a longer time, e.g. when travelling, it is recommended to store insulin in a special cooler bag for medicines or an isolating container from foam or styropore. If stored appropriately the visual nature of insulin must not change. Insulin changed in its visual nature looses its blood sugar lowering effect and must not be used in any case. Take care about it when travelling in summer in hot regions.

More information:
Oral Antidiabetics
Insulin
Types of insulin therapy